
The base-collector junction is reverse biased and provides high resistance in the collector circuit.īefore discussing transistor action, it is important that the reader may keep in mind the following facts about the transistor : The base-emitter junction is forward biased, allowing low resistance for the emit-ter circuit. The middle section which forms two pn-junctions between the emitter and collector is called the base. ( ii), the collector ( n-type) of npn transistor has reverse bias and receives electrons. In Below Fig ( i), the collector ( p-type) of pnp transistor has a reverse bias and receives hole charges that flow in the output circuit. Its function is to remove charges from its junction with the base. The section on the other side that collects the charges is called the collector.
#Type transistor free
( ii), the emitter ( n-type) of npn transistor has a forward bias and supplies free electrons to its junction with the base. ( i), the emitter ( p-type) of pnp transistor is forward biased and supplies hole charges to its junction with the base. base so that it can supply a large number of *majority carriers. The emitter is always forward biased w.r.t. The section on one side that supplies charge carriers (electrons or holes) is called the emitter. The middle section is called the base and forms two junctions between the emitter and collector.
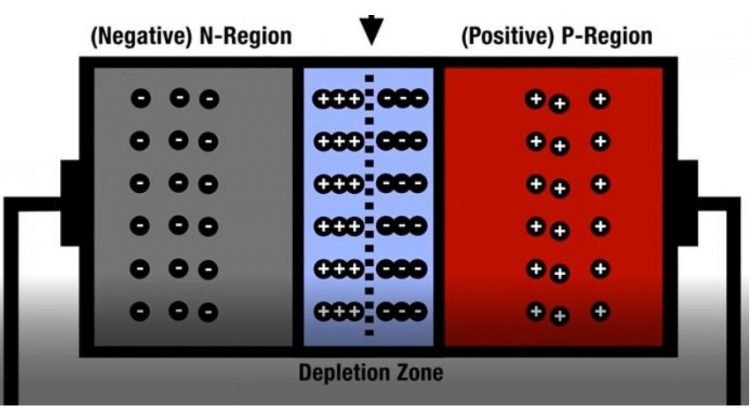
The section on one side is the emitter and the section on the opposite side is the collector. A transistor ( pnp or npn) has three sections of doped semiconductors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
